Introduction
Iron casting products have a wide range of industrial applications due to their durability and strength. The molds used to make these products play a crucial role in ensuring that the final product is of high quality.
In this article, we will explore the different types of iron casting molds material and why using foam materials to make them is advantageous. We will also analyze the pros and cons of using foam materials and provide a step-by-step guide on how to make molds using foam materials.
Applications of Iron Casting Products in Industry
Iron casting products are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery. These products can be found in engines, gears, pipes, and many other components that require strength and durability.
Types of Iron Casting Molds Materials
There are several materials that can be used to make iron casting molds, including:
Aluminum
Aluminum is a common material for creating casting molds because it is lightweight, easy to machine, and has good thermal conductivity. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may not be suitable for certain applications.
Wood
Wood is a traditional material for making casting molds because it is easy to work with and relatively inexpensive. However, it has poor thermal conductivity and may not hold up well to repeated use.
Iron
Cast iron molds are durable and have good heat conductivity. They are typically used for medium to large production runs.
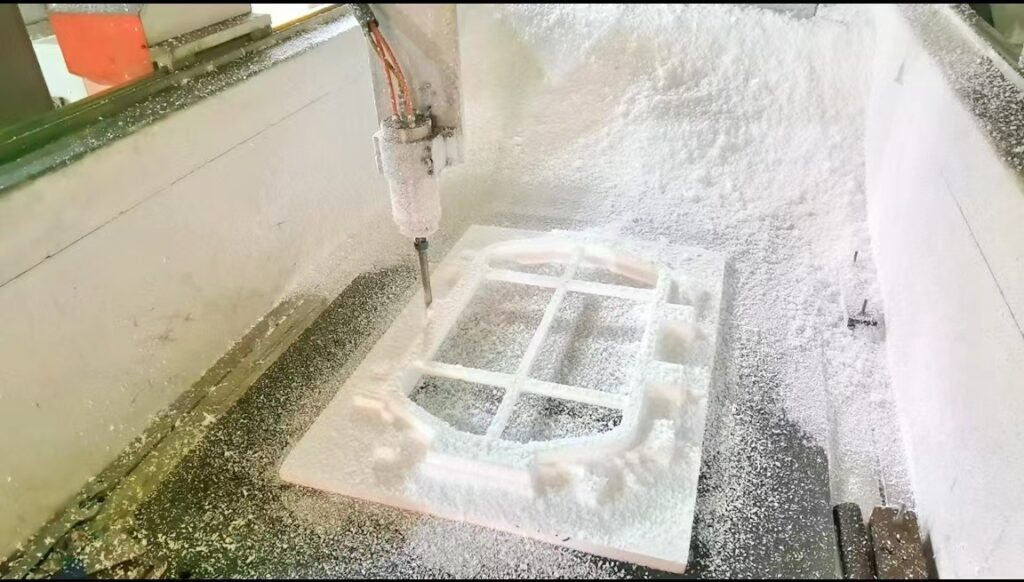
Foam
Foam materials, such as polystyrene or polyurethane foam, have become increasingly popular for creating casting molds in recent years. Foam molds can be easily machined, are cost-effective, and can be molded into complex shapes. However, they have lower thermal conductivity than other materials, which can lead to longer cooling times and lower productivity.
Sand
Sand is the most common material used for creating casting molds, particularly for larger, more complex parts. Molding sand is mixed with a bonding agent and compacted around a pattern to create the mold cavity. Sand molds can be used for a wide range of casting applications and are relatively inexpensive, but they can be time-consuming to prepare and can only be used once.
Why Use Foam Materials to Make Molds
Using foam materials to make molds has several advantages over traditional methods. Foam materials are lightweight, making them easy to handle and transport. They are also easily machinable, which allows for intricate designs to be created. Foam materials are also cost-effective and can be easily molded into any shape.

Pros and Cons of Using Foam Materials
Advantages of Making Iron Casting Molds with Foam Materials:
Lightweight: Foam materials are much lighter than traditional mold materials, making them easier to handle and transport.
Easily Machinable: Foam materials are easily machinable, which allows for intricate designs to be created.
Cost-Effective: Foam materials are relatively inexpensive compared to other mold materials, making them a cost-effective option for creating molds.
Versatile: Foam materials can be easily molded into any shape, making them ideal for creating complex or irregularly shaped molds.
Disadvantages of Making Iron Casting Molds with Foam Materials:
Lower Thermal Conductivity: Foam materials have lower thermal conductivity than traditional mold materials, which can lead to longer cooling times and lower productivity.
Warping and Distortion: Foam materials are more prone to warping and distortion during the casting process, which can affect the quality of the final product.
Fragility: Foam materials are relatively fragile compared to other mold materials, which can make them more prone to damage during handling and transport.
The advantages of using foam materials for molds have already been discussed. However, there are some disadvantages to consider. Foam materials have lower thermal conductivity, which can lead to longer cooling times and lower productivity. They are also more prone to warping and distortion, which can affect the quality of the final product.
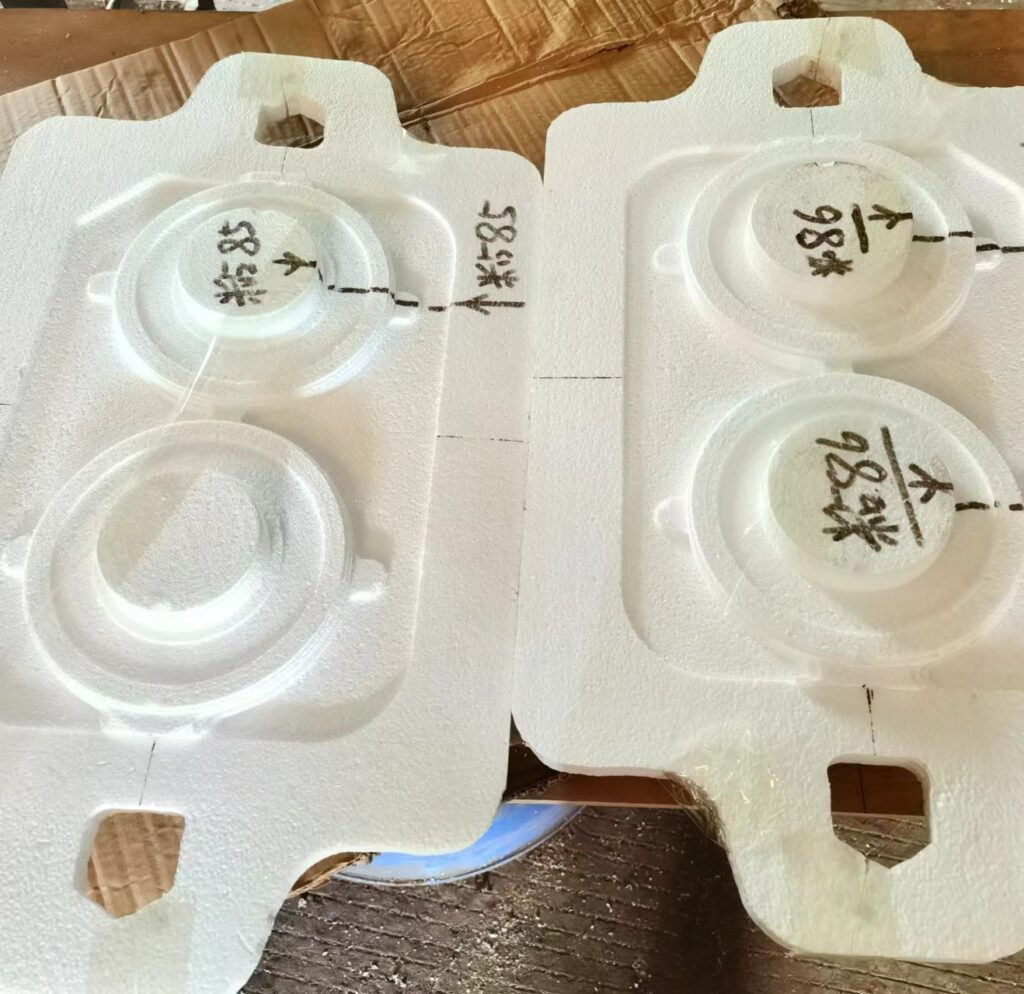

How to Make Molds Using Foam Materials
Here are the detailed steps for making an iron casting mold using foam materials:
Design the Mold
The first step is to design the mold, either manually or using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This includes determining the shape, size, and dimensions of the mold.
Prepare the Foam
Foam blocks or sheets are typically used to create the mold. These can be cut to size using a hot wire cutter or other cutting tool. The foam should be free of any debris or contaminants that could affect the quality of the mold.
Coating the Foam
The foam mold must be coated with a refractory material to protect it from the heat of the molten metal during casting. This coating can be applied using a brush or spray gun. Multiple coats may be necessary to ensure complete coverage.
Embedding the Mold
The coated foam mold is then embedded in a container, such as a flask, to hold it in place during the casting process. The flask is typically filled with a sand or clay mixture, known as molding sand.
Preparing the Molding Sand
The molding sand is prepared by mixing sand with a bonding agent and any other additives needed to achieve the desired properties. The sand is then compacted around the foam mold in the flask.
Removing the Foam
Once the molding sand has set, the foam is removed from the mold by heating it until it vaporizes. This leaves a cavity in the sand, which is then ready for casting.
Pouring the Molten Metal
The molten metal is poured into the mold cavity, filling it completely. The metal is allowed to cool and solidify, forming the final cast iron product.
Finishing the Cast Iron
After the metal has cooled, the casting is removed from the mold and cleaned up as needed. This may involve grinding, sandblasting, or other finishing techniques to remove any excess material or surface imperfections.
Conclusion
Using foam materials to make iron casting molds can offer several advantages over traditional methods. However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and ensure that the foam mold is coated properly to prevent any issues during the casting process. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create high-quality iron casting products efficiently and cost-effectively.
We are Castimoo, a supplier of iron castings. Specializing in the production and sale of grey cast iron and ductile iron, we have over 30 years of experience in the industry. Our customers are all over the world, if you want to purchase iron castings in China, please feel free to contact us.
