Introducion
The performance of an iron casting determines its suitability for a particular application. Sometimes, as small as a part, if the performance is not up to standard, it can cause huge losses.
Therefore, heat treatment is essential to enhance the performance of iron castings.
Heat treatment is a process of heating and cooling the metal to achieve the desired physical and mechanical properties.
In this article, we will introduce some methods of heat treatment for iron castings, as well as explain how to improve the performance of iron castings through heat treatment.
Through the application of these methods, we hope that your iron casting products will meet the performance requirements.
Commonly used heat treatment techniques for iron castings include annealing, tempering, normalizing, austenitic tempering, martensitic tempering and quenching.
Annealing
Annealing reduces the hardness of iron castings and increases ductility by allowing them to absorb more energy.
This is accomplished by heating the casting to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it in an oven or furnace.
When annealing iron castings, it is important to observe the changes in the metal during this process.
The purpose of annealing is to reduce the hardness of the casting and improve its ductility, so it is important to check these properties.
The first step in annealing is to heat the casting to a specific temperature. This temperature will vary depending on the type of iron used. Once the correct temperature is reached, the casting must be allowed to cool slowly in an oven or furnace.
It is important to note that the cooling process should not be rushed, as this can lead to cracks and other defects in the casting. To ensure uniform cooling, the casting should be placed in a preheated oven and allowed to cool slowly for several hours.
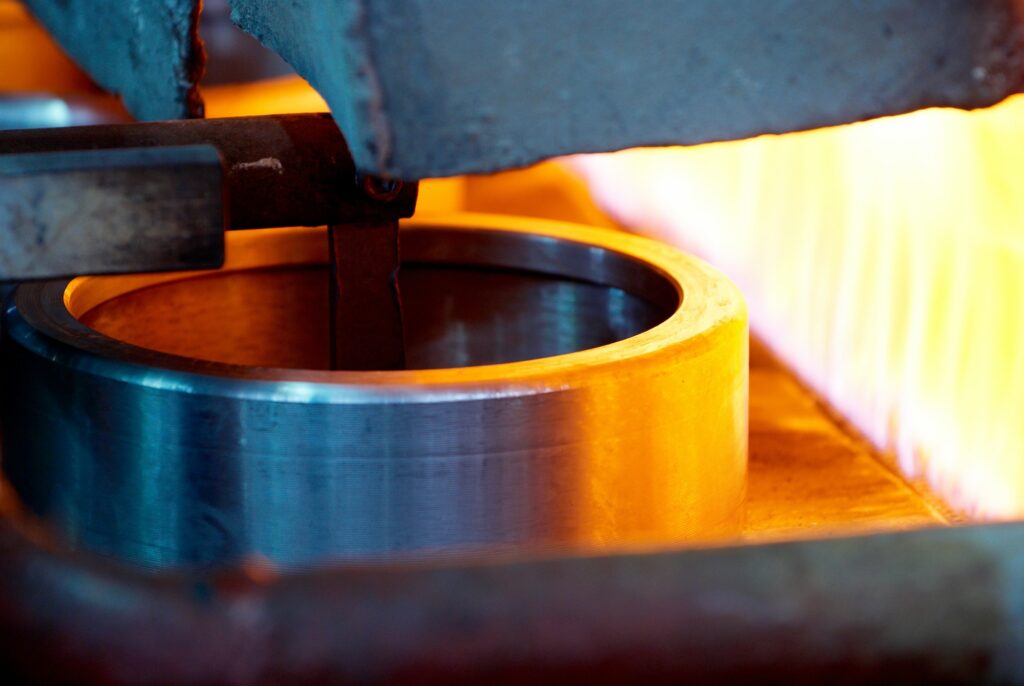

Once cooled, the iron casting will become softer and have better ductility. This will help improve its properties and make it more resistant to wear. With proper annealing, the properties of iron castings can be significantly improved.
Heat treatment is an effective way to improve the performance of iron castings, so this should be taken into account when producing these parts.
With proper annealing, castings will have higher strength, ductility and wear resistance. This makes them ideal for demanding applications and ensures that they perform as expected.
Tempering
Tempering is used to increase the hardness of iron castings while making them tougher. It involves reheating the metal after it has cooled.
The casting is heated to a specific temperature and then allowed to cool again. The amount of time the casting is heated will determine its hardness and toughness.
Tempering of iron castings is an important part of the casting process and should be done carefully to ensure the best results.
When tempering iron castings, it is important to consider the temperature of the metal, as well as the length of time it is heated. The more precise these parameters are, the better the results will be.
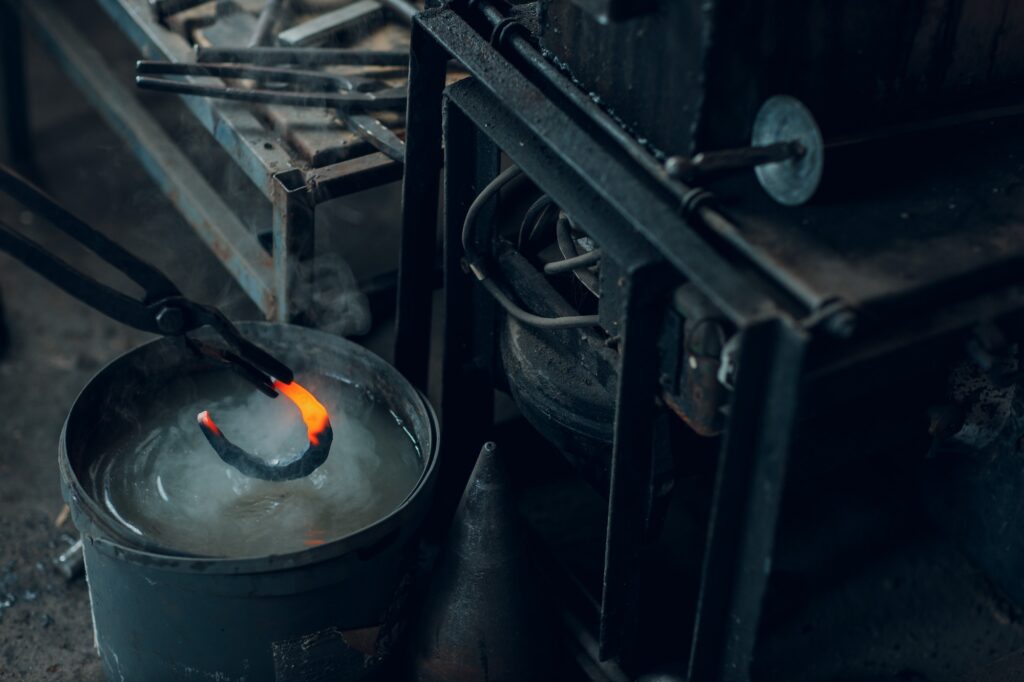

When tempering iron castings, it is also important to use the proper heat treatment equipment. This includes furnaces, quenching tanks and tools for measuring temperature. It is also necessary to keep a record of all the steps taken during the operation to ensure that everything is done correctly.
After tempering the iron casting, it is important to check the hardness of the casting. This can be done with a Rockwell hardness tester and other hardness testing equipment. The results should be compared to the original specifications to ensure that they meet or exceed the expected results.
With proper heat treatment, iron castings can be made stronger and more durable, which will improve their performance in the following applications.
This includes machinery, automotive parts, pumps, valves and other products that require strength and durability.
After the tempering process is complete, the casting should be inspected for any defects to further ensure the performance of the product.
It is important to remember that tempering is a delicate process that requires expertise and experience to get the best results. When done correctly, it can greatly improve the quality of castings used in a variety of applications.
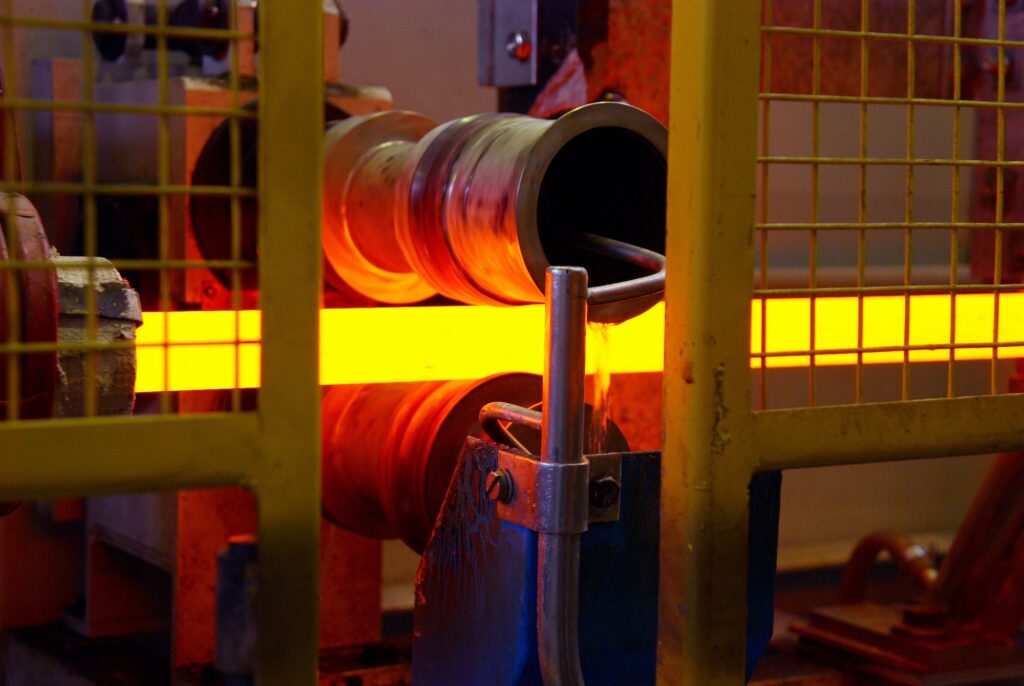

Normalizing
Normalizing involves heating iron castings to a higher temperature than annealing, but not as high as tempering. It is used to reduce the internal stress in the metal and make it more uniform. The casting is then cooled in still air.
When normalizing iron castings, care must be taken with the temperature of the metal and the rate of heating.
The temperature should not exceed the maximum tempering point, as this may lead to embrittlement of the metal and reduce its strength properties. In addition, heating should be carried out at a slow and steady rate.
The rate of cooling of the metal is also important. Too fast a cooling rate can lead to cracking or other problems, while insufficient cooling time can reduce the desired results.
Therefore, castings should be cooled in still air for several hours rather than quenched.
Normalizing heat treatment can improve the properties of iron castings by reducing the internal temperature. It also improves the uniformity of the grain structure and increases the strength properties of the material.
Normalizing is an important step in the production of high quality iron castings and should therefore be carried out carefully, with strict monitoring of temperature and cooling rate to obtain the desired results.

Austenitic Tempering
Austempering is used to increase the toughness of iron castings and make them less brittle. It involves heating the metal to a temperature that hardens it as it cools, and then reheating the metal to a lower temperature.
Austempering is a variant of tempering that holds the metal at a temperature above the critical point of the material before cooling. This results in an increase in strength and toughness without sacrificing ductility or fatigue properties.
When it comes to the austenitic tempering process for iron castings, there are several factors to take into account.
First, the desired properties of the casting must be determined before beginning the process. This includes knowing its intended use, the level of strength and toughness required for its application, and any other factors.
Next, the temperature of the casting must be set correctly. Austenitic tempering is a heat treatment process that involves heating and cooling cycles to achieve the desired properties. When austempering iron castings, thermocouples must be used to obtain accurate temperature readings.

Finally, it is important to monitor the microstructure of the metal during this process. Austempering involves a series of quenching and tempering cycles that affect the mechanical properties of the casting, so it is important to know the results so that the process can be fine-tuned.
Proper use of austempering can improve the performance of iron castings and make them more resistant to wear and corrosion. By carefully monitoring the process, one can ensure that their iron castings have the expected strength and toughness for their intended purpose.
Martempering
Martempering of iron castings is a heat treatment process that involves heating the metal to a specific temperature, followed by quenching and cooling in oil or water.
Martempering involves heat treating the material at a temperature lower than its critical point to increase the strength and wear resistance of the material. It is commonly used for parts that require high levels of durability, such as gears and drive shafts.
There are several key points to consider when martensitically tempering cast iron parts.
First, it is important to ensure that the iron casting is heated to a specific temperature before it is quenched and cooled in oil or water. This will ensure that the tempering process is successful.
Second, the cooling rate should be monitored and controlled as this can affect the properties of the material. It is best to cool the iron casting slowly to achieve the best results.

Third, it is important to choose a solution with a specific oil or water bath. The temperature range of this solution should be appropriate for the size and shape of the iron casting.
Finally, it is important to monitor the effectiveness of the martensitic tempering process by testing the properties of the metal after it has cooled. The hardness, wear resistance, strength and ductility of the metal can be determined by various tests.
By following these steps, the properties of iron castings can be improved.
Martempering helps to bring out the best in the metal, making it suitable for a variety of applications. With careful implementation, martensitic tempering can help create strong and durable iron castings that are resistant to wear and tear.
Quenching
Quenching is used to increase the strength of iron castings by rapid cooling. It is accomplished by heating the metal to a specific temperature and then cooling it in water or oil.
It is important to note that the quenching process should be done properly, as improper quenching can cause warping, cracking or distortion. To obtain the best results, the correct temperature and cooling medium must be selected.
For quenching, the iron casting should be heated to a specific temperature and then cooled in water or oil. The temperature range varies depending on the type of metal being used.

Once the iron has been heated to the desired temperature, it must be cooled quickly by immersing it in either of the following two media: water or oil.
Water quenching is the most common method of improving the strength of iron castings because it cools the metal quickly and uniformly. However, if tight tolerances need to be met, oil quenching should be used, as it allows for more precise control of cooling time and temperature.
The strength of iron castings can be significantly improved by quenching. It is important to remember that this process should be carried out properly in order to achieve the desired results.
Careful selection of the combination of temperature and cooling medium is critical to the successful heat treatment of iron castings.
By understanding how to improve the performance of iron castings, manufacturers can produce higher quality products that are stronger and more durable.
Conclusion
This article discusses six common types of heat treatments. They are annealing, tempering, normalizing, austenitic tempering, martensitic tempering, and quenching.
Heat treatment is an important step in improving the performance of a product.
By applying different heat treatment techniques, the performance of your iron casting products can be improved to make them suitable for all types of applications. Heat treatment can also help reduce production costs and ensure that the metal has a longer life.
Be sure to select the correct heat treatment technique for your specific needs and make sure it is done correctly to get the best results.
By applying these methods correctly, you can ensure that the performance of your iron casting products is improved.
Castimoo has specialized in the production of gray cast iron and ductile iron for 30 years. If you are looking for a supplier of iron castings, please feel free to contact us.

2 Responses
Thanks for sharing!
Appreciated!